Martin Cífka
CIIRC/CTU, Prague.

I am a Ph.D. student in the Intelligent Machine Perception group with the Czech Institute of Informatics, Robotics and Cybernetics (CIIRC, CTU Prague) under the supervision of Josef Šivic. I obtained my M.Sc. degree in Visual Computing at Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Charles University in Prague (MFF, CUNI) in 2024. My research interests include 6D pose estimation and object detection in an uncontrolled environment.
selected publications
-
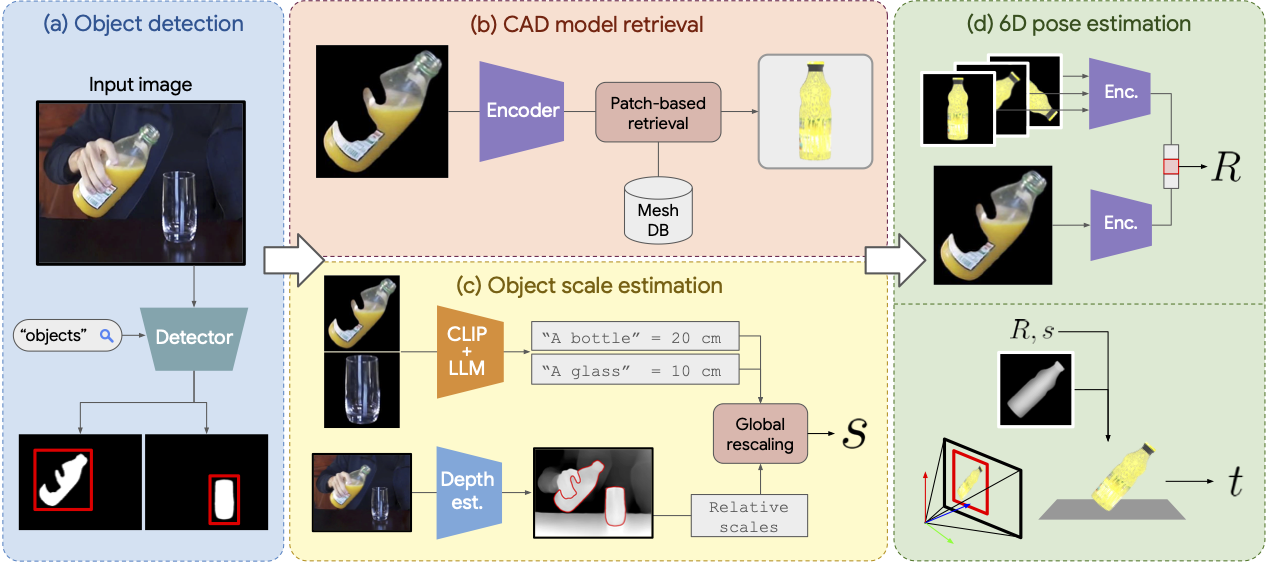 6D Object Pose Tracking in Internet Videos for Robotic ManipulationGeorgy Ponimatkin, Martin Cífka, Tomas Soucek, and 4 more authorsIn The Thirteenth International Conference on Learning Representations, 2025
6D Object Pose Tracking in Internet Videos for Robotic ManipulationGeorgy Ponimatkin, Martin Cífka, Tomas Soucek, and 4 more authorsIn The Thirteenth International Conference on Learning Representations, 2025We seek to extract a temporally consistent 6D pose trajectory of a manipulated object from an Internet instructional video. This is a challenging set-up for current 6D pose estimation methods due to uncontrolled capturing conditions, subtle but dynamic object motions, and the fact that the exact mesh of the manipulated object is not known. To address these challenges, we present the following contributions. First, we develop a new method that estimates the 6D pose of any object in the input image without prior knowledge of the object itself. The method proceeds by (i) retrieving a CAD model similar to the depicted object from a large-scale model database, (ii) 6D aligning the retrieved CAD model with the input image, and (iii) grounding the absolute scale of the object with respect to the scene. Second, we extract smooth 6D object trajectories from Internet videos by carefully tracking the detected objects across video frames. The extracted object trajectories are then retargeted via trajectory optimization into the configuration space of a robotic manipulator. Third, we thoroughly evaluate and ablate our 6D pose estimation method on YCB-V and HOPE-Video datasets as well as a new dataset of instructional videos manually annotated with approximate 6D object trajectories. We demonstrate significant improvements over existing state-of-the-art RGB 6D pose estimation methods. Finally, we show that the 6D object motion estimated from Internet videos can be transferred to a 7-axis robotic manipulator both in a virtual simulator as well as in a real world set-up. We also successfully apply our method to egocentric videos taken from the EPIC-KITCHENS dataset, demonstrating potential for Embodied AI applications.
@inproceedings{ponimatkin2025d, title = {{{6D}} {{Object}} {{Pose}} {{Tracking}} in {{Internet}} {{Videos}} for {{Robotic}} {{Manipulation}}}, author = {Ponimatkin, Georgy and C{\'i}fka, Martin and Soucek, Tomas and Fourmy, M{\'e}d{\'e}ric and Labb{\'e}, Yann and Petrik, Vladimir and Sivic, Josef}, booktitle = {The Thirteenth International Conference on Learning Representations}, year = {2025}, } -
 FocalPose++: Focal Length and Object Pose Estimation via Render and CompareMartin Cífka, Georgy Ponimatkin, Yann Labbé, and 4 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2025
FocalPose++: Focal Length and Object Pose Estimation via Render and CompareMartin Cífka, Georgy Ponimatkin, Yann Labbé, and 4 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2025We introduce FocalPose++, a neural render-and-compare method for jointly estimating the camera-object 6D pose and camera focal length given a single RGB input image depicting a known object. The contributions of this work are threefold. First, we derive a focal length update rule that extends an existing state-of-the-art render-and-compare 6D pose estimator to address the joint estimation task. Second, we investigate several different loss functions for jointly estimating the object pose and focal length. We find that a combination of direct focal length regression with a reprojection loss disentangling the contribution of translation, rotation, and focal length leads to improved results. Third, we explore the effect of different synthetic training data on the performance of our method. Specifically, we investigate different distributions used for sampling object’s 6D pose and camera’s focal length when rendering the synthetic images, and show that parametric distribution fitted on real training data works the best. We show results on three challenging benchmark datasets that depict known 3D models in uncontrolled settings. We demonstrate that our focal length and 6D pose estimates have lower error than the existing state-of-the-art methods.
@article{cifka2024focalpose++, title = {{F}ocal{P}ose++: {F}ocal {L}ength and {O}bject {P}ose {E}stimation via {R}ender and {C}ompare}, author = {C{\'i}fka, Martin and Ponimatkin, Georgy and Labb{\'e}, Yann and Russell, Bryan and Aubry, Mathieu and Petrik, Vladimir and Sivic, Josef}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence}, year = {2025}, volume = {47}, number = {2}, pages = {755-772}, doi = {10.1109/TPAMI.2024.3475638}, } -
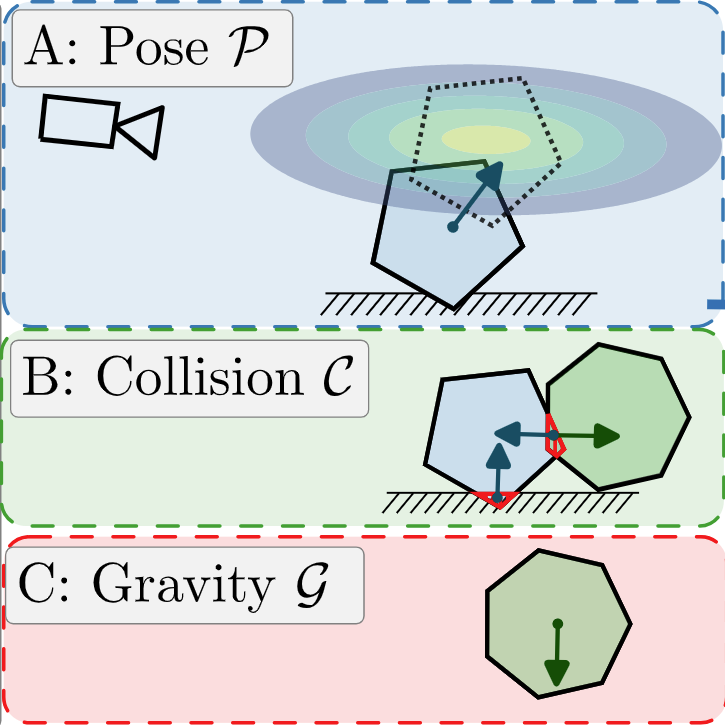 PhysPose: Refining 6D Object Poses with Physical ConstraintsMartin Malenický, Martin Cífka, Médéric Fourmy, and 4 more authorsarXiv preprint arXiv:2503.23587, 2025
PhysPose: Refining 6D Object Poses with Physical ConstraintsMartin Malenický, Martin Cífka, Médéric Fourmy, and 4 more authorsarXiv preprint arXiv:2503.23587, 2025Accurate 6D object pose estimation from images is a key problem in object-centric scene understanding, enabling applications in robotics, augmented reality, and scene reconstruction. Despite recent advances, existing methods often produce physically inconsistent pose estimates, hindering their deployment in real-world scenarios. We introduce PhysPose, a novel approach that integrates physical reasoning into pose estimation through a postprocessing optimization enforcing non-penetration and gravitational constraints. By leveraging scene geometry, PhysPose refines pose estimates to ensure physical plausibility. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art accuracy on the YCB-Video dataset from the BOP benchmark and improves over the state-of-the-art pose estimation methods on the HOPE-Video dataset. Furthermore, we demonstrate its impact in robotics by significantly improving success rates in a challenging pick-and-place task, highlighting the importance of physical consistency in real-world applications.
@article{malenicky2025physpose, title = {{P}hys{P}ose: {R}efining 6{D} {O}bject {P}oses with {P}hysical {C}onstraints}, author = {Malenick{\'y}, Martin and C{\'i}fka, Martin and Fourmy, M{\'e}d{\'e}ric and Montaut, Louis and Carpentier, Justin and Sivic, Josef and Petrik, Vladimir}, journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2503.23587}, year = {2025}, } -
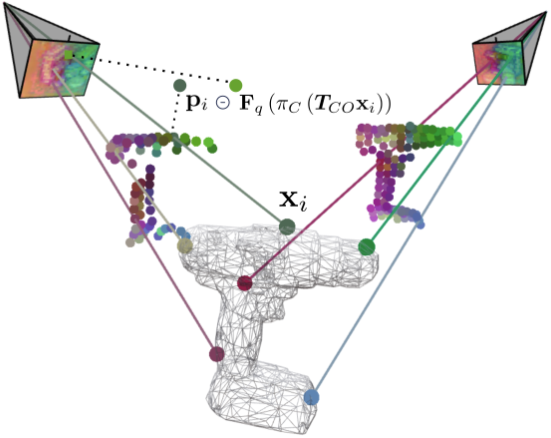 AlignPose: Generalizable 6D Pose Estimation via Multi-view Feature-metric AlignmentAnna Š. Mikeštíková, Médéric Fourmy, Martin Cífka, and 2 more authorsarXiv preprint arXiv:2512.20538, 2025
AlignPose: Generalizable 6D Pose Estimation via Multi-view Feature-metric AlignmentAnna Š. Mikeštíková, Médéric Fourmy, Martin Cífka, and 2 more authorsarXiv preprint arXiv:2512.20538, 2025Single-view RGB model-based object pose estimation methods achieve strong generalization but are fundamentally limited by depth ambiguity, clutter, and occlusions. Multi-view pose estimation methods have the potential to solve these issues, but existing works rely on precise single-view pose estimates or lack generalization to unseen objects. We address these challenges via the following three contributions. First, we introduce AlignPose, a 6D object pose estimation method that aggregates information from multiple extrinsically calibrated RGB views and does not require any object-specific training or symmetry annotation. Second, the key component of this approach is a new multi-view feature-metric refinement specifically designed for object pose. It optimizes a single, consistent world-frame object pose minimizing the feature discrepancy between on-the-fly rendered object features and observed image features across all views simultaneously. Third, we report extensive experiments on four datasets (YCB-V, T-LESS, ITODD-MV, HouseCat6D) using the BOP benchmark evaluation and show that AlignPose outperforms other published methods, especially on challenging industrial datasets where multiple views are readily available in practice.
@article{mikevstikova2025alignpose, title = {{A}lign{P}ose: {G}eneralizable 6{D} {P}ose {E}stimation via {M}ulti-view {F}eature-metric {A}lignment}, author = {Mike{\v{s}}t{\'i}kov{\'a}, Anna {\v{S}}. and Fourmy, M{\'e}d{\'e}ric and C{\'i}fka, Martin and Sivic, Josef and Petrik, Vladimir}, journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2512.20538}, year = {2025}, }